Every summer before school was over, I was assigned a list of books to read. Mostly nonfiction and historical fiction, but in fourth grade there that was that first science fiction book. I often remember how that book made me feel, and marvel at the impact that it had in my life. I had read some science fiction before—Well’s Time Traveller and War of the Worlds—but this was different. This was a book with witty and thought-provoking short stories by Isaac Asimov. Each of them delivered drama, comedy, mystery and a surprise ending in about ten pages. And they had robots. And those robots had personalities, in spite of their very simple programming: The Three Laws of Robotics.
- A robot may not injure a human being or, through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm.
- A robot must obey the orders given to it by human beings, except where such orders would conflict with the First Law.
- A robot must protect its own existence as long as such protection does not conflict with the First or Second Law.
Back in the 1980s, robotics—understood as autonomous mechanical thinking—was no more than a dream. A wonderful dream that fueled many children’s imaginations and probably shaped the career choices of some. I know in my case it did.
Fast forward some thirty-odd years, when I met Astro: one of three research robots manufactured by the French company Aldebaran. This NAO robot found its way into the computer science classroom of Tom Simpson in Heathwood Hall Episcopal School, and quickly learned to navigate mazes, recognize some student’s faces and names, and even dance the Macarena! It did so with effortless coding: a basic command of the computer language python, and some idea of object oriented programming.
I could not let this opportunity pass. I created a small undergraduate team with Danielle Talley from USC (a brilliant sophomore in computer engineering, with a minor in music), and two math majors from Morris College: my Geometry expert Fabian Maple, and a McGyver-style problem solver, Wesley Alexander. Wesley and Fabian are supported by a Department of Energy-Environmental Management grant to Morris College, which funds their summer research experience at USC. Danielle is funded by the National Science Foundation through the Louis Stokes South Carolina-Alliance for Minority Participation (LS-SCAMP).
They spent the best of their first week on this project completing a basic programming course online. At the same time, the four of us reviewed some of the mathematical tools needed to teach Astro new tricks: basic algebra and trigonometry, basic geometry, and basic calculus and statistics. The emphasis—I need to point out in case you missed it—is in the word basic.

Talk the talk
The psychologist seated herself and watched Herbie narrowly as he took a chair at the other side of the table and went through the three books systematically.
At the end of half an hour, he put them down, “Of course, I know why you brought these.”
The corner of Dr. Calvin’s lip twitched, “I was afraid you would. It’s difficult to work with you, Herbie. You’re always a step ahead of me.”
“It’s the same with these books, you know, as with the others. They just don’t interest me. There’s nothing to your textbooks. Your science is just a mass of collected data plastered together by makeshift theory — and all so incredibly simple, that it’s scarcely worth bothering about.”
“It’s your fiction that interests me. Your studies of the interplay of human motives and emotions” – his mighty hand gestured vaguely as he sought the proper words.
Liar!
— Isaac Asimov
Astro can understand what I say, and maintain conversations with me. He has four microphones for voice recognition and sound localization, and two speakers for text-to-speech synthesis. But he sometimes gets confused: I say “acute”, and he understands “abide,” for example. This might sound frustrating by all standards. But mathematicians can’t be judged by any reasonable standard. Far from seeing this as a shortcoming, my team used as motivation the mechanics behind his speech recognition functionality, and they wrote some code to turn him into an expert Mastermind player.
Wait, what? How are these two things possibly connected?
Since Astro’s hearing is far from perfect, when he hears a word which is not clear, he gathers a short list of possible candidates. He then chooses the most likely guess based upon different considerations—using clues from context, for example. Based on similar strategies, he can be taught to be a perfect player of 5-letter-word Mastermind: Pick any five-letter word in the English language. Any word, provided it has no repeated letters. Astro chooses one random word as his first guess, and requests a score like in Mastermind.
To illustrate this process, I will show you how the game went when I chose Fabian’s favorite word: “acute.”
Astro: Is it firth?
Me : NO
Astro: How many letters of my guess are in your word, in the right position?
How many letters of my guess are in your word, in the wrong position?
Me : 1, 0
Astro: Is it foams?
Me : NO
Astro: How many letters of my guess are in your word, in the right position?
How many letters of my guess are in your word, in the wrong position?
Me : 0, 1
Astro: Is it junta?
Me : NO
Astro: How many letters of my guess are in your word, in the right position?
How many letters of my guess are in your word, in the wrong position?
Me : 1, 2
Astro: Is it acute?
Me : YES
Astro: Wonderful, I found it in 4 attempts!
I don’t want to get too technical here, but will mention some of the ideas. The main algorithm is based on techniques of numerical root finding and solving nonlinear equations — nothing complex: high-school level bracketing by bisection, or Newton’s method. To design better winning strategies, my team exploits the benefits of randomness. The analysis of this part is done with basic probability and statistics.
Walk the walk
Donovan’s pencil pointed nervously. “The red cross is the selenium pool. You marked it yourself.”
“Which one is it?” interrupted Powell. “There were three that MacDougal located for us before he left.”
“I sent Speedy to the nearest, naturally; seventeen miles away. But what difference does that make?” There was tension in his voice. “There are penciled dots that mark Speedy’s position.”
And for the first time Powell’s artificial aplomb was shaken and his hands shot forward for the man.
“Are you serious? This is impossible.”
“There it is,” growled Donovan.
The little dots that marked the position formed a rough circle about the red cross of the selenium pool. And Powell’s fingers went to his brown mustache, the unfailing signal of anxiety.
Donovan added: “In the two hours I checked on him, he circled that damned pool four times. It seems likely to me that he’ll keep that up forever. Do you realize the position we’re in?”
Runaround
— Isaac Asimov
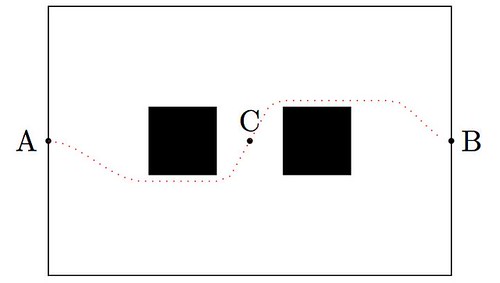
Astro moves around too. It does so thanks to a sophisticated system combining one accelerometer, one gyrometer and four ultrasonic sensors that provide him with stability and positioning within space. He also enjoys eight force-sensing resistors and two bumpers. And that is only for his legs! He can move his arms, bend his elbows, open and close his hands, or move his torso and neck (up to 25 degrees of freedom for the combination of all possible joints). Out of the box, and without much effort, he can be coded to walk around, although in a mechanical way: He moves forward a few feet, stops, rotates in place or steps to a side, etc. A very naïve way to go from A to B retrieving an object at C, could be easily coded in this fashion as the diagram shows:

Fabian and Wesley devised a different way to code Astro taking full advantage of his inertial measurement unit. This will allow him to move around smoothly, almost like a human would. The key to their success? Polynomial interpolation and plane geometry. For advanced solutions, they need to learn about splines, curvature, and optimization. Nothing they can’t handle.
Sing me a song
He said he could manage three hours and Mortenson said that would be perfect when I gave him the news. We picked a night when she was going to be singing Bach or Handel or one of those old piano-bangers, and was going to have a long and impressive solo.
Mortenson went to the church that night and, of course, I went too. I felt responsible for what was going to happen and I thought I had better oversee the situation.
Mortenson said, gloomily, “I attended the rehearsals. She was just singing the same way she always did; you know, as though she had a tail and someone was stepping on it.”
One Night of Song
— Isaac Asimov
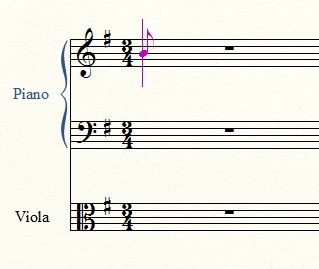
Astro has excellent eyesight and understanding of the world around him. He is equipped with two HD cameras, and a bunch of computer vision algorithms, including facial and shape recognition. Danielle’s dream is to have him read from a music sheet and sing or play the song in a toy piano. She is very close to completing this project: Astro is able now to identify partitures, and extract from them the location of the pentagrams. Danielle is currently working on identifying the notes and the clefs. This is one of her test images, and the result of one of her early experiments:
Most of the techniques Danielle is using are accessible to any student with a decent command of vector calculus, and enough scientific maturity. The extraction of pentagrams and the different notes on them, for example, is performed with the Hough transform. This is a fancy term for an algorithm that basically searches for straight lines and circles by solving an optimization problem in two or three variables.
The only thing left is an actual performance. Danielle will be leading Fabian and Wes, and with the assistance of Mr. Simpson’s awesome students Erica and Robert, Astro will hopefully learn to physically approach the piano, choose the right keys, and play them in the correct order and speed. Talent show, anyone?
with no smoothness or structure assumptions a priori. Most relevant information of a given image is contained in the contours of the mapped objects: Think for example of a bright object against a dark background—the area where these two meet presents a curve where the intensity
varies strongly. This is what we refer to as an “edge.”

This gradient should have a large intensity
and a direction
which indicates the perpendicular to the curve. It therefore looks sound to simply compute the gradient of
and choose the points where these values are large. This conclusion is a bit unrealistic for two reasons:




(left), find a script that constructs a good approximation to its structural model (right).